The Role of Oceans in Regulating Climate
Climate change is one of the major challenges facing the world today, and the ocean, as Earth's largest body of water, plays a crucial role in climate change. The ocean and climate are inextricably linked, influencing and interacting with each other.
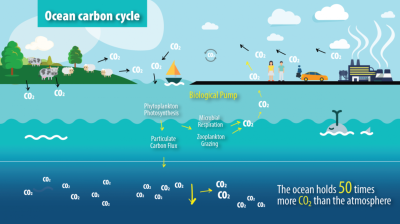
- Heat absorption by the ocean: Due to its vast surface area, the ocean's waters have a strong ability to absorb solar radiation. Most of this solar radiation reaching Earth is absorbed by the ocean, making it Earth's largest reservoir of heat energy.
- Heat storage and release: Because the ocean absorbs a large amount of solar radiation, the temperature of the seawater remains relatively stable. During the day, the seawater absorbs heat, causing its temperature to rise; at night, it releases heat, causing its temperature to cool. This heat storage and release process helps regulate Earth's climate.
- The ocean's influence on the atmosphere: Water evaporates from the ocean surface, forming water vapor that enters the atmosphere. This water vapor condenses in the air, forming clouds and subsequently precipitation. Furthermore, the ocean influences atmospheric temperature by releasing latent heat.
- The influence of ocean currents on climate: Ocean currents are a crucial component of the ocean water cycle, carrying heat from equatorial regions to higher latitudes, thereby influencing global climate. For example, the famous Gulf Stream brings warm weather to Europe.
- Interactions between the Atmosphere and the Ocean: Complex interactions exist between the ocean and the atmosphere. The ocean influences the atmosphere by releasing heat, water vapor, and latent heat; the atmosphere, in turn, influences the ocean through processes such as wind and precipitation. This interaction helps regulate Earth's climate.

- Sea Level Rise
- Ocean Acidification
- Extreme Weather Events




